Introduction to Microservices
Typically, the application structure is based on a monolithic architecture scheme. In this architecture, all the elements implemented are included in a single application. The monolithic architecture has some disadvantages, such as it becomes more difficult to solve problems and add new functionalities as the application grows. The microservicies architecture pattern is proposed in order to solve these problems.
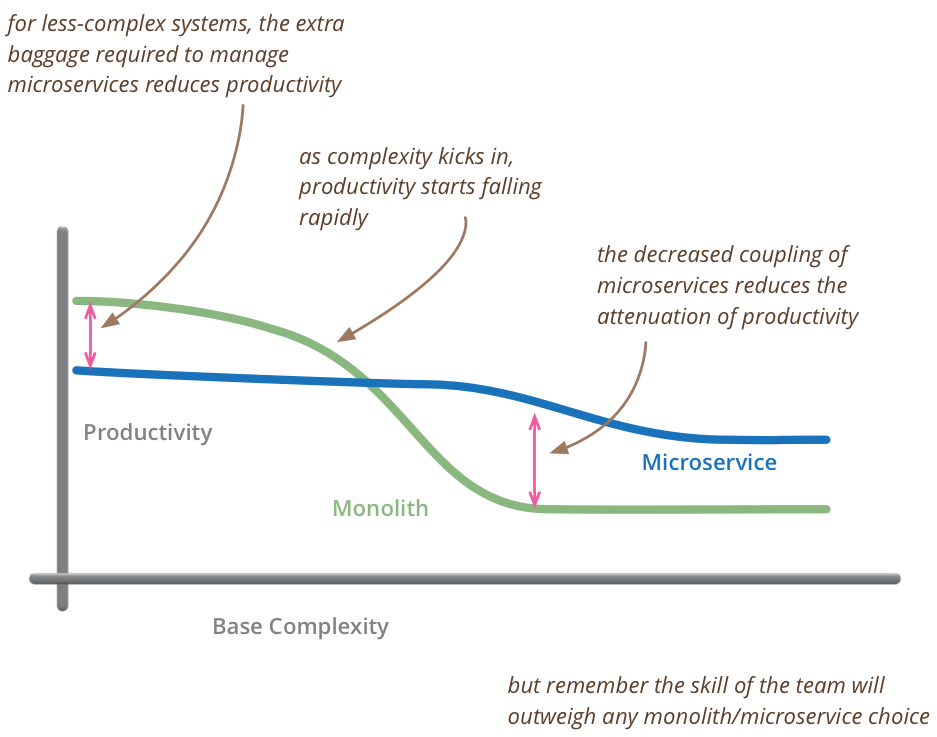
Figure 1: Microservice vs Monolith architecture. Source: Martin Fowler
What are the microservices?
Microservices - also known as the microservice architecture - structures an application as a collection of services. The idea is to split the application into a set of smaller, interconnected services instead of building a single monolithic application. Thus, each microservice is a small application.
Ideally, a microservice or service has to be specialized in solving the problems of a single domain using the best available technology. In addition, each service must have an API in order to facilitate communication and interaction with the other microservices. The microservices architecture propose a new type of relationship between the application and the database. Instead of sharing a single database schema with other services, each service has its own database schema. Having a database schema per service is essential if you want to benefit from microservices, because it ensures loose coupling.
Normally, the communication with the client is mediated by an intermediary known as an API Gateway. The API Gateway is responsible for tasks such as load balancing, caching, access control, API metering, and monitoring.
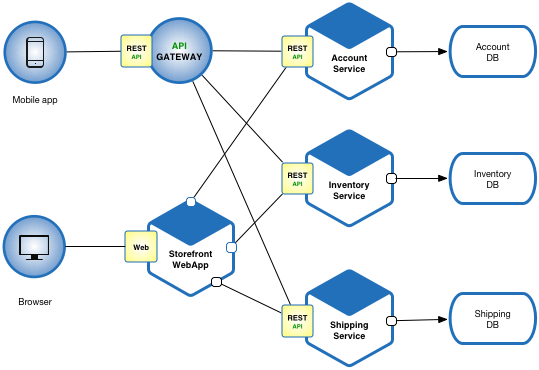
Figure 2: Example of application implemented following the microservices architecture. Source: Microservices.io
Companies using microservice architecture: Netflix, Amazon, Ebay, Uber, Sound Cloud, etc.
Beneficts
- If one microservice fails, the whole system does not crash
- Facilitates scalability of the application.
- Gives developers the freedom to independently develop and deploy services.
- Different programming languages can be used in different modules.
- Easy to maintain, modify and reuse.
- The most recommended technology can be used for each problem.
- Easy to scale and manage development teams.
Disadvantages
- Testing can be difficult due to distributed deployment.
- If the design is not done properly, this architecture could lead with latency problems, load balancing, etc.
- High memory consumption
- Complexity in integrating and managing a large number of services.
- The members of a development group must have good background training.